Troubleshooting Startup and Login Items
- WireGuard On The Mac App Store
- How To Boot In Single User Mode On A Mac - OS X Daily
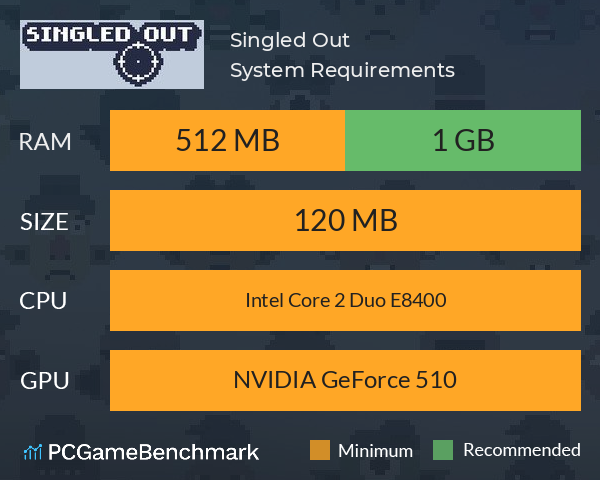
- Sengled Out Mac Os Download
- Sengled Out Mac Os X
This FAQ, derived from our book Troubleshooting Mac® OS X, provides a procedure for determining if Startup Items or Login Items may be the cause of a problem.
Switching between Mac and Windows Operating System:- You can go back and forth between macOS and Windows on your Mac, but you can't run both OS simultaneously under Boot Camp. Instead, you have to boot one operating system or the other — thus, the name Boot Camp. Restart your Mac, and hold down the Option key until icons for each operating. Mac Pro, OS X Mountain Lion (10.8.3) Posted on Apr 4, 2013 4:36 PM Reply I have this question too (25) I have this question too Me too (25) Me too.
Corrupted or incompatible Startup or Login Items can cause a variety of problems, including:
- Kernel panics.
- Finder™ crashes on startup or login, either once or repeatedly.
- Slow startup or login.
- Failed startup or login
Third-party interface modifications — hacks or 'haxies '— and menu extras — the icons on the right side of the Apple menu bar under Mac OS X 10.3 and later — are often launched as Startup or Login Items.
The use of the terms Startup Items and Login Items has varied between versions of Mac OS X:
- The term Startup Items has been used consistently in Mac OS X for system-wide applications or processes launched at startup and before any users log in to their accounts.
- The term for account-specific applications or processes launched when a user logs in to their account has varied from Mac OS X 10.2 to 10.4, as follows:
- Mac OS X 10.2 Jaguar, Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger®, and later use the term Login Items.
- Mac OS X 10.3 Panther® uses the term Startup Items.
Beginning in Tiger, the direction has been to replace Startup Items with daemons and user agents managed by the launchd process. Like Startup Items, daemons are background processes that provide services to all users; user agents — agents for short — are background processes that provide services to one or more users. The move to daemons and agents gained substantial momentum in Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard®. Advice on troubleshooting daemons and agents is covered in our book Troubleshooting Mac OS X, Leopard Edition.
| 1. | Start up in Safe Mode. |
To identify if incompatible Startup or Login items are causing problems, start up in Safe Mode. If Safe Boot resolves the issue, this implies a Startup Item or Login Item is the cause. Follow the remaining steps in this procedure to determine the specific Startup or Login Items at fault. Note that Safe Mode has certain operating limitations. Under Tiger, any fonts you disabled using Font Book will be enabled when you next restart or log in to your Mac. | |
| 2. | Rule out third-party interface modifications and menu extras. |
If you are using third-party interface modifications or menu extras: Shotgun christmas mac os.
If this resolves the problem, report the problem to the developer or vendor of the application causing the problem. | |
| 3. | Troubleshoot account-specific Startup or Login Items. |
Account-specific Startup Items (Panther) or Login Items (Tiger, Jaguar) are launched when a user logs in to their account. They are used to launch specific applications or open specific documents or folders when the user logs in to their account. You define account-specific Startup Items (Panther) or Login Items (Tiger or Jaguar) for your account as follows:
Third-party applications may add items to these lists. Troubleshoot these via process-of-elimination:
| |
| 4. | Troubleshoot system-wide Startup Items. |
Third-party applications may install system-wide Startup Items in the Computer > Macintosh HD > Library > StartupItems folder. System-wide Startup Items are launched when you start up your Mac and before any users can log in to their accounts. They are used to start system-wide processes that should be run before users log in to their accounts, such as anti-virus software, or to launch system-wide processes that can be available to all users, such as a background process used by a third-party application. Troubleshoot these via process-of-elimination:
|
Related links
- Finder issues? How to delete its preferences.
- Resolving Kernel Panics.
- Tuning Mac OS X Performance.
To use a keyboard shortcut, press and hold one or more modifier keys and then press the last key of the shortcut. For example, to use Command-C (copy), press and hold the Command key, then the C key, then release both keys. Mac menus and keyboards often use symbols for certain keys, including modifier keys:
On keyboards made for Windows PCs, use the Alt key instead of Option, and the Windows logo key instead of Command.
Some keys on some Apple keyboards have special symbols and functions, such as for display brightness , keyboard brightness , Mission Control, and more. If these functions aren't available on your keyboard, you might be able to reproduce some of them by creating your own keyboard shortcuts. To use these keys as F1, F2, F3, or other standard function keys, combine them with the Fn key.
Cut, copy, paste, and other common shortcuts
- Command-X: Cut the selected item and copy it to the Clipboard.
- Command-C: Copy the selected item to the Clipboard. This also works for files in the Finder.
- Command-V: Paste the contents of the Clipboard into the current document or app. This also works for files in the Finder.
- Command-Z: Undo the previous command. You can then press Shift-Command-Z to Redo, reversing the undo command. In some apps, you can undo and redo multiple commands.
- Command-A: Select All items.
- Command-F: Find items in a document or open a Find window.
- Command-G: Find Again: Find the next occurrence of the item previously found. To find the previous occurrence, press Shift-Command-G.
- Command-H: Hide the windows of the front app. To view the front app but hide all other apps, press Option-Command-H.
- Command-M: Minimize the front window to the Dock. To minimize all windows of the front app, press Option-Command-M.
- Command-O: Open the selected item, or open a dialog to select a file to open.
- Command-P: Print the current document.
- Command-S: Save the current document.
- Command-T: Open a new tab.
- Command-W: Close the front window. To close all windows of the app, press Option-Command-W.
- Option-Command-Esc: Force quit an app.
- Command–Space bar: Show or hide the Spotlight search field. To perform a Spotlight search from a Finder window, press Command–Option–Space bar. (If you use multiple input sources to type in different languages, these shortcuts change input sources instead of showing Spotlight. Learn how to change a conflicting keyboard shortcut.)
- Control–Command–Space bar: Show the Character Viewer, from which you can choose emoji and other symbols.
- Control-Command-F: Use the app in full screen, if supported by the app.
- Space bar: Use Quick Look to preview the selected item.
- Command-Tab: Switch to the next most recently used app among your open apps.
- Shift-Command-5: In macOS Mojave or later, take a screenshot or make a screen recording. Or use Shift-Command-3 or Shift-Command-4 for screenshots. Learn more about screenshots.
- Shift-Command-N: Create a new folder in the Finder.
- Command-Comma (,): Open preferences for the front app.
Sleep, log out, and shut down shortcuts
You might need to press and hold some of these shortcuts for slightly longer than other shortcuts. This helps you to avoid using them unintentionally.
WireGuard On The Mac App Store
- Power button: Press to turn on your Mac or wake it from sleep. Press and hold for 1.5 seconds to put your Mac to sleep.* Continue holding to force your Mac to turn off.
- Option–Command–Power button* or Option–Command–Media Eject : Put your Mac to sleep.
- Control–Shift–Power button* or Control–Shift–Media Eject : Put your displays to sleep.
- Control–Power button* or Control–Media Eject : Display a dialog asking whether you want to restart, sleep, or shut down.
- Control–Command–Power button:* Force your Mac to restart, without prompting to save any open and unsaved documents.
- Control–Command–Media Eject : Quit all apps, then restart your Mac. If any open documents have unsaved changes, you will be asked whether you want to save them.
- Control–Option–Command–Power button* or Control–Option–Command–Media Eject : Quit all apps, then shut down your Mac. If any open documents have unsaved changes, you will be asked whether you want to save them.
- Control-Command-Q: Immediately lock your screen.
- Shift-Command-Q: Log out of your macOS user account. You will be asked to confirm. To log out immediately without confirming, press Option-Shift-Command-Q.
* Does not apply to the Touch ID sensor.
Finder and system shortcuts
- Command-D: Duplicate the selected files.
- Command-E: Eject the selected disk or volume.
- Command-F: Start a Spotlight search in the Finder window.
- Command-I: Show the Get Info window for a selected file.
- Command-R: (1) When an alias is selected in the Finder: show the original file for the selected alias. (2) In some apps, such as Calendar or Safari, refresh or reload the page. (3) In Software Update preferences, check for software updates again.
- Shift-Command-C: Open the Computer window.
- Shift-Command-D: Open the desktop folder.
- Shift-Command-F: Open the Recents window, showing all of the files you viewed or changed recently.
- Shift-Command-G: Open a Go to Folder window.
- Shift-Command-H: Open the Home folder of the current macOS user account.
- Shift-Command-I: Open iCloud Drive.
- Shift-Command-K: Open the Network window.
- Option-Command-L: Open the Downloads folder.
- Shift-Command-N: Create a new folder.
- Shift-Command-O: Open the Documents folder.
- Shift-Command-P: Show or hide the Preview pane in Finder windows.
- Shift-Command-R: Open the AirDrop window.
- Shift-Command-T: Show or hide the tab bar in Finder windows.
- Control-Shift-Command-T: Add selected Finder item to the Dock (OS X Mavericks or later)
- Shift-Command-U: Open the Utilities folder.
- Option-Command-D: Show or hide the Dock.
- Control-Command-T: Add the selected item to the sidebar (OS X Mavericks or later).
- Option-Command-P: Hide or show the path bar in Finder windows.
- Option-Command-S: Hide or show the Sidebar in Finder windows.
- Command–Slash (/): Hide or show the status bar in Finder windows.
- Command-J: Show View Options.
- Command-K: Open the Connect to Server window.
- Control-Command-A: Make an alias of the selected item.
- Command-N: Open a new Finder window.
- Option-Command-N: Create a new Smart Folder.
- Command-T: Show or hide the tab bar when a single tab is open in the current Finder window.
- Option-Command-T: Show or hide the toolbar when a single tab is open in the current Finder window.
- Option-Command-V: Move the files in the Clipboard from their original location to the current location.
- Command-Y: Use Quick Look to preview the selected files.
- Option-Command-Y: View a Quick Look slideshow of the selected files.
- Command-1: View the items in the Finder window as icons.
- Command-2: View the items in a Finder window as a list.
- Command-3: View the items in a Finder window in columns.
- Command-4: View the items in a Finder window in a gallery.
- Command–Left Bracket ([): Go to the previous folder.
- Command–Right Bracket (]): Go to the next folder.
- Command–Up Arrow: Open the folder that contains the current folder.
- Command–Control–Up Arrow: Open the folder that contains the current folder in a new window.
- Command–Down Arrow: Open the selected item.
- Right Arrow: Open the selected folder. This works only when in list view.
- Left Arrow: Close the selected folder. This works only when in list view.
- Command-Delete: Move the selected item to the Trash.
- Shift-Command-Delete: Empty the Trash.
- Option-Shift-Command-Delete: Empty the Trash without confirmation dialog.
- Command–Brightness Down: Turn video mirroring on or off when your Mac is connected to more than one display.
- Option–Brightness Up: Open Displays preferences. This works with either Brightness key.
- Control–Brightness Up or Control–Brightness Down: Change the brightness of your external display, if supported by your display.
- Option–Shift–Brightness Up or Option–Shift–Brightness Down: Adjust the display brightness in smaller steps. Add the Control key to this shortcut to make the adjustment on your external display, if supported by your display.
- Option–Mission Control: Open Mission Control preferences.
- Command–Mission Control: Show the desktop.
- Control–Down Arrow: Show all windows of the front app.
- Option–Volume Up: Open Sound preferences. This works with any of the volume keys.
- Option–Shift–Volume Up or Option–Shift–Volume Down: Adjust the sound volume in smaller steps.
- Option–Keyboard Brightness Up: Open Keyboard preferences. This works with either Keyboard Brightness key.
- Option–Shift–Keyboard Brightness Up or Option–Shift–Keyboard Brightness Down: Adjust the keyboard brightness in smaller steps.
- Option key while double-clicking: Open the item in a separate window, then close the original window.
- Command key while double-clicking: Open a folder in a separate tab or window.
- Command key while dragging to another volume: Move the dragged item to the other volume, instead of copying it.
- Option key while dragging: Copy the dragged item. The pointer changes while you drag the item.
- Option-Command while dragging: Make an alias of the dragged item. The pointer changes while you drag the item.
- Option-click a disclosure triangle: Open all folders within the selected folder. This works only when in list view.
- Command-click a window title: See the folders that contain the current folder.
- Learn how to use Command or Shift to select multiple items in the Finder.
- Click the Go menu in the Finder menu bar to see shortcuts for opening many commonly used folders, such as Applications, Documents, Downloads, Utilities, and iCloud Drive.
Document shortcuts
The behavior of these shortcuts may vary with the app you're using.
- Command-B: Boldface the selected text, or turn boldfacing on or off.
- Command-I: Italicize the selected text, or turn italics on or off.
- Command-K: Add a web link.
- Command-U: Underline the selected text, or turn underlining on or off.
- Command-T: Show or hide the Fonts window.
- Command-D: Select the Desktop folder from within an Open dialog or Save dialog.
- Control-Command-D: Show or hide the definition of the selected word.
- Shift-Command-Colon (:): Display the Spelling and Grammar window.
- Command-Semicolon (;): Find misspelled words in the document.
- Option-Delete: Delete the word to the left of the insertion point.
- Control-H: Delete the character to the left of the insertion point. Or use Delete.
- Control-D: Delete the character to the right of the insertion point. Or use Fn-Delete.
- Fn-Delete: Forward delete on keyboards that don't have a Forward Delete key. Or use Control-D.
- Control-K: Delete the text between the insertion point and the end of the line or paragraph.
- Fn–Up Arrow: Page Up: Scroll up one page.
- Fn–Down Arrow: Page Down: Scroll down one page.
- Fn–Left Arrow: Home: Scroll to the beginning of a document.
- Fn–Right Arrow: End: Scroll to the end of a document.
- Command–Up Arrow: Move the insertion point to the beginning of the document.
- Command–Down Arrow: Move the insertion point to the end of the document.
- Command–Left Arrow: Move the insertion point to the beginning of the current line.
- Command–Right Arrow: Move the insertion point to the end of the current line.
- Option–Left Arrow: Move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous word.
- Option–Right Arrow: Move the insertion point to the end of the next word.
- Shift–Command–Up Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the beginning of the document.
- Shift–Command–Down Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the end of the document.
- Shift–Command–Left Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the beginning of the current line.
- Shift–Command–Right Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the end of the current line.
- Shift–Up Arrow: Extend text selection to the nearest character at the same horizontal location on the line above.
- Shift–Down Arrow: Extend text selection to the nearest character at the same horizontal location on the line below.
- Shift–Left Arrow: Extend text selection one character to the left.
- Shift–Right Arrow: Extend text selection one character to the right.
- Option–Shift–Up Arrow: Extend text selection to the beginning of the current paragraph, then to the beginning of the following paragraph if pressed again.
- Option–Shift–Down Arrow: Extend text selection to the end of the current paragraph, then to the end of the following paragraph if pressed again.
- Option–Shift–Left Arrow: Extend text selection to the beginning of the current word, then to the beginning of the following word if pressed again.
- Option–Shift–Right Arrow: Extend text selection to the end of the current word, then to the end of the following word if pressed again.
- Control-A: Move to the beginning of the line or paragraph.
- Control-E: Move to the end of a line or paragraph.
- Control-F: Move one character forward.
- Control-B: Move one character backward.
- Control-L: Center the cursor or selection in the visible area.
- Control-P: Move up one line.
- Control-N: Move down one line.
- Control-O: Insert a new line after the insertion point.
- Control-T: Swap the character behind the insertion point with the character in front of the insertion point.
- Command–Left Curly Bracket ({): Left align.
- Command–Right Curly Bracket (}): Right align.
- Shift–Command–Vertical bar (|): Center align.
- Option-Command-F: Go to the search field.
- Option-Command-T: Show or hide a toolbar in the app.
- Option-Command-C: Copy Style: Copy the formatting settings of the selected item to the Clipboard.
- Option-Command-V: Paste Style: Apply the copied style to the selected item.
- Option-Shift-Command-V: Paste and Match Style: Apply the style of the surrounding content to the item pasted within that content.
- Option-Command-I: Show or hide the inspector window.
- Shift-Command-P: Page setup: Display a window for selecting document settings.
- Shift-Command-S: Display the Save As dialog, or duplicate the current document.
- Shift–Command–Minus sign (-): Decrease the size of the selected item.
- Shift–Command–Plus sign (+): Increase the size of the selected item. Command–Equal sign (=) performs the same function.
- Shift–Command–Question mark (?): Open the Help menu.
How To Boot In Single User Mode On A Mac - OS X Daily
Other shortcuts
Sengled Out Mac Os Download
For more shortcuts, check the shortcut abbreviations shown in the menus of your apps. Every app can have its own shortcuts, and shortcuts that work in one app might not work in another.
- Apple Music shortcuts: Choose Help > Keyboard shortcuts from the menu bar in the Music app.
- Other shortcuts: Choose Apple menu > System Preferences, click Keyboard, then click Shortcuts.
Learn more
Sengled Out Mac Os X
- Create your own shortcuts and resolve conflicts between shortcuts
- Change the behavior of the function keys or modifier keys

